中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (41): 6684-6688.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.41.022
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
维甲酸和睾酮单独与联合诱导脂肪源干细胞周期的变化
段富华,曾文钦,杨 春,杨会营,余美春,陶 晖,戴景兴,原 林
- 南方医科大学人体解剖学教研室,广东省广州市 510515
Retinoic acid, testosterone or their combination affects the cell cycle of adipose-derived stem cells
Duan Fu-hua, Zeng Wen-qin, Yang Chun, Yang Hui-ying, Yu Mei-chun, Tao Hui, Dai Jing-xing, Yuan Lin
- Department of Human Anatomy, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
背景:目前关于维甲酸对干细胞增殖作用的研究较少见,对睾酮的研究主要集中于其抑制细胞衰老的作用方面。
目的:探索维甲酸和睾酮单独和联合诱导对脂肪源干细胞细胞周期的影响。
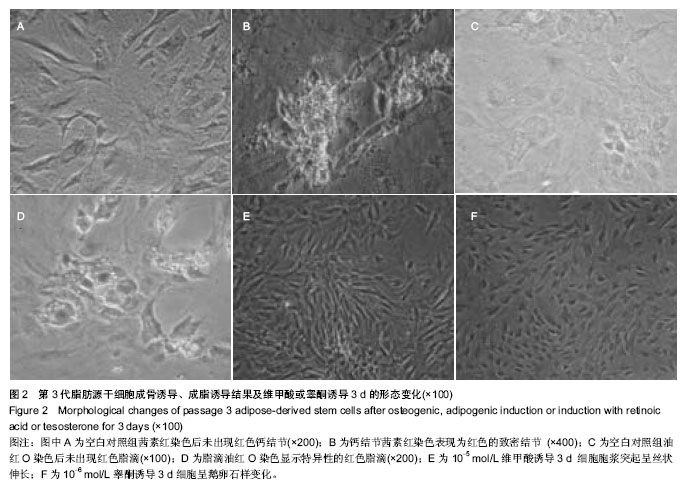
方法:分离培养2月龄SD雌性大鼠脂肪源干细胞,传至第3代进行成脂、成骨诱导和表面标记鉴定。将其分为6组:①对照组。②10-5 mol/L 维甲酸组。③10-6 mol/L 维甲酸组。④10-5 mol/L维甲酸+睾酮组。⑤10-6 mol/L维甲酸+睾酮组。⑥睾酮组。对照组应用DMEM+体积分数10%胎牛血清培养液,其余各组均在对照组的基础上加相应剂量维甲酸或睾酮或二者联合诱导剂。各组培养36 h后行流式细胞仪检测各细胞分期的变化。
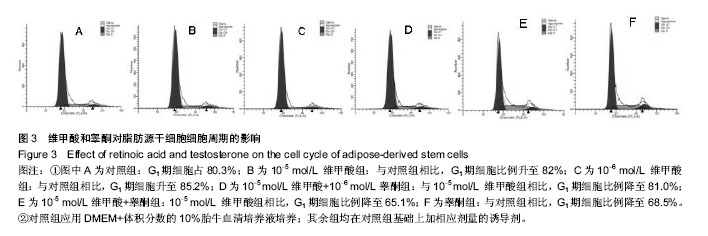
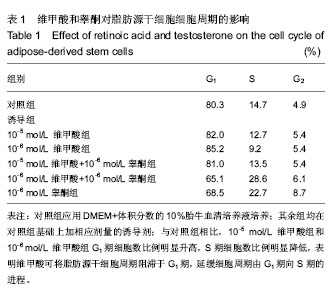
结果与结论:与对照组相比,10-5 mol/L 维甲酸组和10-6 mol/L 维甲酸组G1期细胞数比例明显升高,S期细胞数比例明显降低。与对照组相比,睾酮组G1期细胞数比例明显下降,S期细胞数比例为明显上升。10-5 mol/L维甲酸+睾酮组与10-5 mol/L 维甲酸组比较,10-6 mol/L维甲酸+睾酮组与10-6 mol/L 维甲酸组比较,G1期细胞数比例有所下降,S期细胞数比例为明显上升。结果表明,维甲酸可将脂肪源干细胞周期阻滞于G1期,延缓细胞周期由G1期向S期的进程;睾酮可加速脂肪源干细胞周期由G1期向S期的进程;联合诱导可加速脂肪源干细胞的细胞周期由G1期向S期的进程。
中图分类号:

.jpg)